 A French pilot study suggests that preoperative acupuncture administered to the ear, reduces the dose of drugs needed to achieve subsequent general anaesthesia. A total of 32 patients aged 18 to 65 awaiting elective digestive or gynaecological surgery, were allocated to receive either acupuncture or no acupuncture as a control group. Needles were retained for 20 minutes before administering conventional anaesthetics. The required dose was 18% lower in the acupuncture group. The study authors believe acupuncture may exert its effects in this case via the vagus nerve and parasympathetic nervous system.
A French pilot study suggests that preoperative acupuncture administered to the ear, reduces the dose of drugs needed to achieve subsequent general anaesthesia. A total of 32 patients aged 18 to 65 awaiting elective digestive or gynaecological surgery, were allocated to receive either acupuncture or no acupuncture as a control group. Needles were retained for 20 minutes before administering conventional anaesthetics. The required dose was 18% lower in the acupuncture group. The study authors believe acupuncture may exert its effects in this case via the vagus nerve and parasympathetic nervous system.
(Effect of Auricular Acupuncture on Propofol Induction Dose: Could Vagus Nerve and Parasympathetic Stimulation Replace Intravenous Co-Induction Agents? Medical Acupuncture, 15 April 2019.)

 Acupuncture combined with amiodarone, a standard anti-arrhythmic drug, seems more effective at preventing the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after ablation, than does the drug alone. A Chinese team randomised 85 patients into acupuncture and control groups. Both groups used the drug from day one after the ablation, but additionally the acupuncture group received daily needling for seven days afterwards.
Acupuncture combined with amiodarone, a standard anti-arrhythmic drug, seems more effective at preventing the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after ablation, than does the drug alone. A Chinese team randomised 85 patients into acupuncture and control groups. Both groups used the drug from day one after the ablation, but additionally the acupuncture group received daily needling for seven days afterwards. A Cochrane Database systematic review by Italian authors looking at acupuncture for prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, has concluded that based on short term follow up, acupuncture reduces prostatitis symptoms in an appreciable number of participants compared with sham procedure. In an appreciable number of patients, it probably also decreases prostatitis symptoms when compared with standard medical therapy. In all, the authors examined 38 studies covering 3300 men, which made 23 comparisons between different treatment and lifestyle interventions.
A Cochrane Database systematic review by Italian authors looking at acupuncture for prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, has concluded that based on short term follow up, acupuncture reduces prostatitis symptoms in an appreciable number of participants compared with sham procedure. In an appreciable number of patients, it probably also decreases prostatitis symptoms when compared with standard medical therapy. In all, the authors examined 38 studies covering 3300 men, which made 23 comparisons between different treatment and lifestyle interventions. A Chinese research team looking at whether acupuncture benefits prostatitis, has concluded it offers long-lasting and clinically significant improvements for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. A total of 68 men aged 18 to 50, were randomised to receive either eight weeks of acupuncture or eight weeks of non-insertive sham needling. Both groups were followed up for a further 24 weeks.
A Chinese research team looking at whether acupuncture benefits prostatitis, has concluded it offers long-lasting and clinically significant improvements for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. A total of 68 men aged 18 to 50, were randomised to receive either eight weeks of acupuncture or eight weeks of non-insertive sham needling. Both groups were followed up for a further 24 weeks. 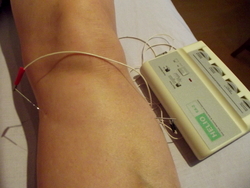 Authors of a study undertaken in Korea have concluded that electro-acupuncture should be recommended as a non-pharmacological treatment for the pain of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A total of 126 patients with the condition were randomly assigned to either electro-acupuncture or to a non-treatment control group. Treatment was given twice a week for eight weeks. Both groups were given dietary and lifestyle advice, diabetes medication and painkillers (paracetamol) to use when required.
Authors of a study undertaken in Korea have concluded that electro-acupuncture should be recommended as a non-pharmacological treatment for the pain of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A total of 126 patients with the condition were randomly assigned to either electro-acupuncture or to a non-treatment control group. Treatment was given twice a week for eight weeks. Both groups were given dietary and lifestyle advice, diabetes medication and painkillers (paracetamol) to use when required.